How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate surveying tasks. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This guide will equip you with the essential understanding and techniques needed to safely and effectively pilot your drone, whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your existing expertise.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and safety regulations to advanced flight maneuvers and post-flight maintenance.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, camera settings, and flight planning, providing step-by-step instructions and practical tips along the way. By the end, you’ll be confident in your ability to navigate the skies and capture stunning visuals with your drone.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and legal repercussions. This section details the essential steps and safety regulations to ensure a successful and safe flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal requirements, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you operate your drone safely and responsibly.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is vital. This involves several key steps to ensure your drone is in optimal condition.
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight time, and ensure the battery is properly connected and shows no signs of damage (swelling, leakage).
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, chips, or any signs of damage. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Verification: Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and unstable flight.
- Gimbal and Camera Check: Check the gimbal for smooth movement and the camera for proper functionality. Ensure the lens is clean and free from obstructions.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts, damage, or unusual wear and tear.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. This includes understanding and respecting airspace restrictions, maintaining visual line of sight, and flying safely away from populated areas.
- Always obtain necessary permits and licenses before operating a drone in regulated airspace.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Avoid flying near airports, stadiums, or other restricted areas.
- Never fly over crowds or people.
- Be aware of local laws and regulations concerning drone operation.
- Always fly responsibly and respectfully.
Emergency Procedures
Having a plan for emergencies is essential. Knowing who to contact and what steps to take can mitigate potential problems and ensure safety.
| Emergency | Procedure | Contact Information | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone malfunction | Initiate emergency landing procedure (refer to drone manual). | Drone manufacturer’s support | Attempt a controlled descent if possible. |
| Loss of signal | Attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, initiate RTH (Return to Home) function. | Local authorities (if necessary) | Monitor drone location until it lands. |
| Accident or incident | Secure the area, document the event, and report to relevant authorities. | Local law enforcement, FAA (or equivalent in your region) | Gather any relevant evidence. |
| Battery failure | Initiate RTH (Return to Home) function immediately if available. If not, perform a controlled emergency landing. | N/A | Prioritize safe landing over data recovery. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section provides a guide to basic controls and flight modes.
Basic Drone Controls, How to operate a drone
Most drones utilize a similar control scheme. Understanding these basic controls is the first step towards mastering drone piloting.
- Throttle: Controls the altitude of the drone (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s forward and backward movement.
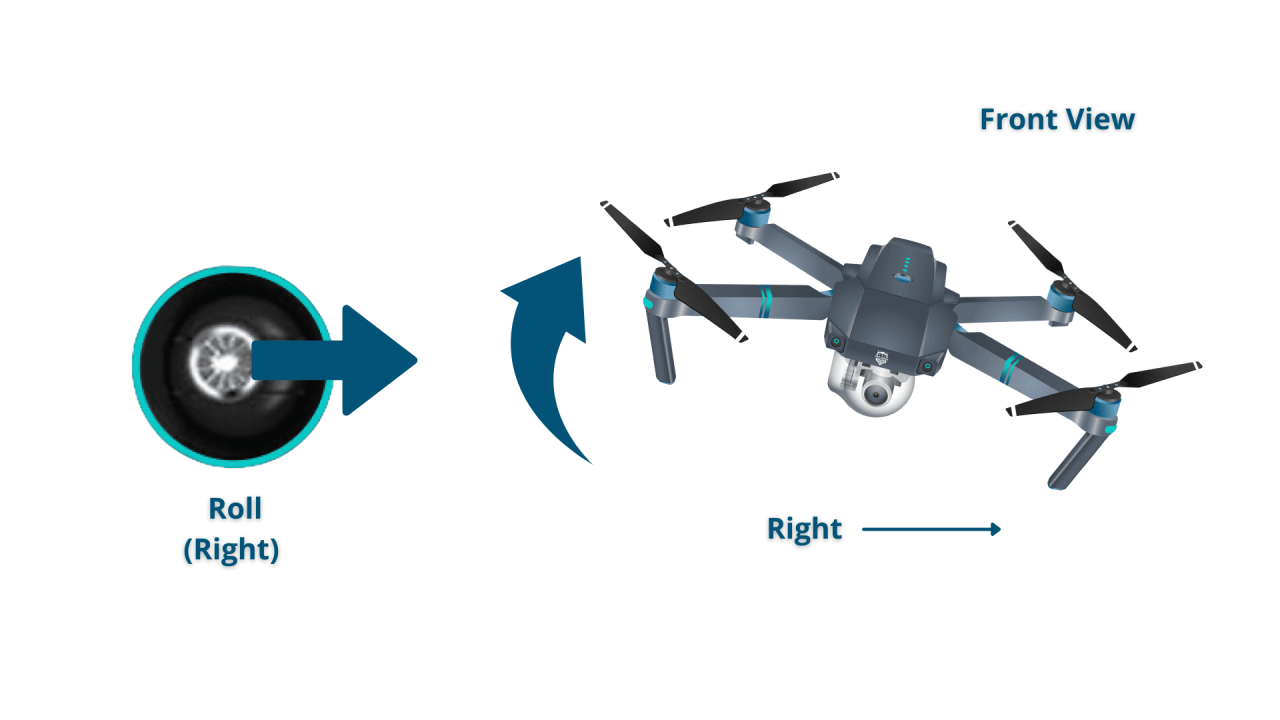
- Roll: Controls the drone’s side-to-side movement.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Selecting the appropriate mode enhances safety and control.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning the basics.
- Sport Mode: Allows for faster speeds and more agile maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for precise positioning and stability, helpful for longer flights and complex maneuvers.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of GPS signal.
Stable Flight and Obstacle Avoidance
Maintaining stable flight and avoiding obstacles requires practice and awareness. These tips can significantly improve your piloting skills.
- Start with short practice flights in open areas with minimal obstacles.
- Gradually increase flight duration and complexity as your skills improve.
- Use the drone’s obstacle avoidance features (if available).
- Maintain a safe distance from obstacles.
- Always be aware of your surroundings.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering these basic maneuvers is crucial for confident drone operation. Practice each maneuver until you feel comfortable and in control.
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground.
- Landing: Slowly decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady altitude and position by carefully adjusting the throttle.
- Directional Movement: Use the pitch and roll controls to move the drone forward, backward, left, and right.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera settings is key to capturing high-quality images and videos. This section explores camera settings and image formats.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Adjusting camera settings allows for optimization of image quality based on lighting conditions and desired effects.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values are better for bright conditions, while higher values are needed in low light, but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) allows more light in, resulting in a shallower depth of field (blurred background).
- White Balance: Adjusts the colors to accurately reflect the scene’s lighting conditions.
- Exposure Compensation: Allows for manual adjustments to the overall brightness of the image.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
The process of capturing high-quality media involves careful consideration of various factors.
- Lighting: Shoot during the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds for visually appealing shots.
- Steady Shots: Minimize camera shake by using a tripod or gimbal.
- Focus: Ensure your subject is in sharp focus.
- Post-Processing: Edit your images and videos to enhance their quality.
Image Formats
Different image formats offer varying levels of quality and file size. Choosing the right format depends on your needs and workflow.
- JPEG: A compressed format, offering good quality with smaller file sizes. Ideal for quick sharing and online use.
- RAW: An uncompressed format, retaining maximum image data. Allows for greater flexibility in post-processing but results in larger file sizes.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Flight planning software is instrumental in safe and efficient drone operation, especially for complex flights. Careful planning ensures optimal flight performance and minimizes risks.
Importance of Flight Planning Software
Flight planning software allows for pre-flight visualization of the flight path, ensuring safety and efficiency. It helps avoid obstacles and stay within legal airspace boundaries.
Factors to Consider When Planning a Flight

Several key factors must be considered when planning a drone flight to ensure a successful and safe operation.
- Weather Conditions: Wind speed, precipitation, and visibility significantly impact drone flight.
- Airspace Restrictions: Check for any airspace restrictions in your flight area using resources like B4UFLY (or your region’s equivalent).
- Battery Life: Calculate the required flight time and ensure sufficient battery power for the entire mission, including a buffer for unexpected situations.
- Flight Path: Plan a safe and efficient flight path, avoiding obstacles and restricted areas.
Creating a Flight Plan
Creating a flight plan typically involves defining waypoints, setting altitude and speed, and reviewing the planned path for safety.
- Define Waypoints: Set the desired locations (waypoints) for the drone to fly to.
- Set Altitude and Speed: Specify the desired altitude and speed for each segment of the flight.
- Review Flight Path: Carefully review the planned flight path to ensure it is safe and avoids obstacles and restricted areas.
- Simulate Flight (if possible): Many software packages allow for simulation before actual flight to identify potential issues.
- Upload Flight Plan: Upload the finalized flight plan to your drone.
Elements of a Typical Flight Plan
A typical flight plan visually shows a series of waypoints connected by lines, representing the drone’s intended path. Each waypoint is marked with its coordinates and altitude. The plan also indicates the drone’s starting and ending points, along with altitude and speed profiles for each leg of the flight. The visual representation provides a clear overview of the entire mission, allowing for adjustments before execution.
The plan might also incorporate no-fly zones as shaded areas, clearly highlighting areas to avoid.
Post-Flight Procedures and Drone Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are essential for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your drone. This section Artikels the necessary steps.
Post-Flight Procedures
Following these steps after each flight helps maintain your drone’s health and ensures data integrity.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation.
- Landing: Perform a safe and controlled landing in a designated area.
- Battery Storage: Store batteries in a safe and appropriate location, away from heat and moisture. Allow them to cool before storage.
- Data Transfer: Download any captured photos and videos to your computer or storage device.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a final visual inspection for any damage or loose parts.
Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and extends the life of your drone. A consistent maintenance schedule is crucial.
- Propeller Cleaning: Clean propellers regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Body Cleaning: Wipe down the drone body with a soft, damp cloth.
- Gimbal Calibration: Calibrate the gimbal periodically to maintain its accuracy.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
- Battery Care: Store batteries properly and avoid extreme temperatures.
Maintenance Checklist

This checklist summarizes recommended maintenance tasks and their frequencies.
- Daily: Visual inspection for damage, battery check.
- Weekly: Propeller cleaning, body cleaning.
- Monthly: Gimbal calibration, firmware updates.
- Quarterly: More thorough inspection, potential motor lubrication (check your drone’s manual).
Operating a drone successfully combines technical proficiency with responsible piloting. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the essential steps, from pre-flight preparation to post-flight maintenance. By diligently following safety guidelines and mastering the techniques discussed, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial flight. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a skilled and responsible drone pilot.
Embrace the journey, and enjoy the incredible perspectives that await you.
FAQ Insights
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes per battery charge, often less in colder temperatures or with heavy camera use.
What is the legal framework for flying drones?
Drone regulations vary by country and region. It’s crucial to research and understand local laws and obtain any necessary permits or licenses before flying.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements also depend on your location. Check with your national aviation authority for specific rules and procedures.
